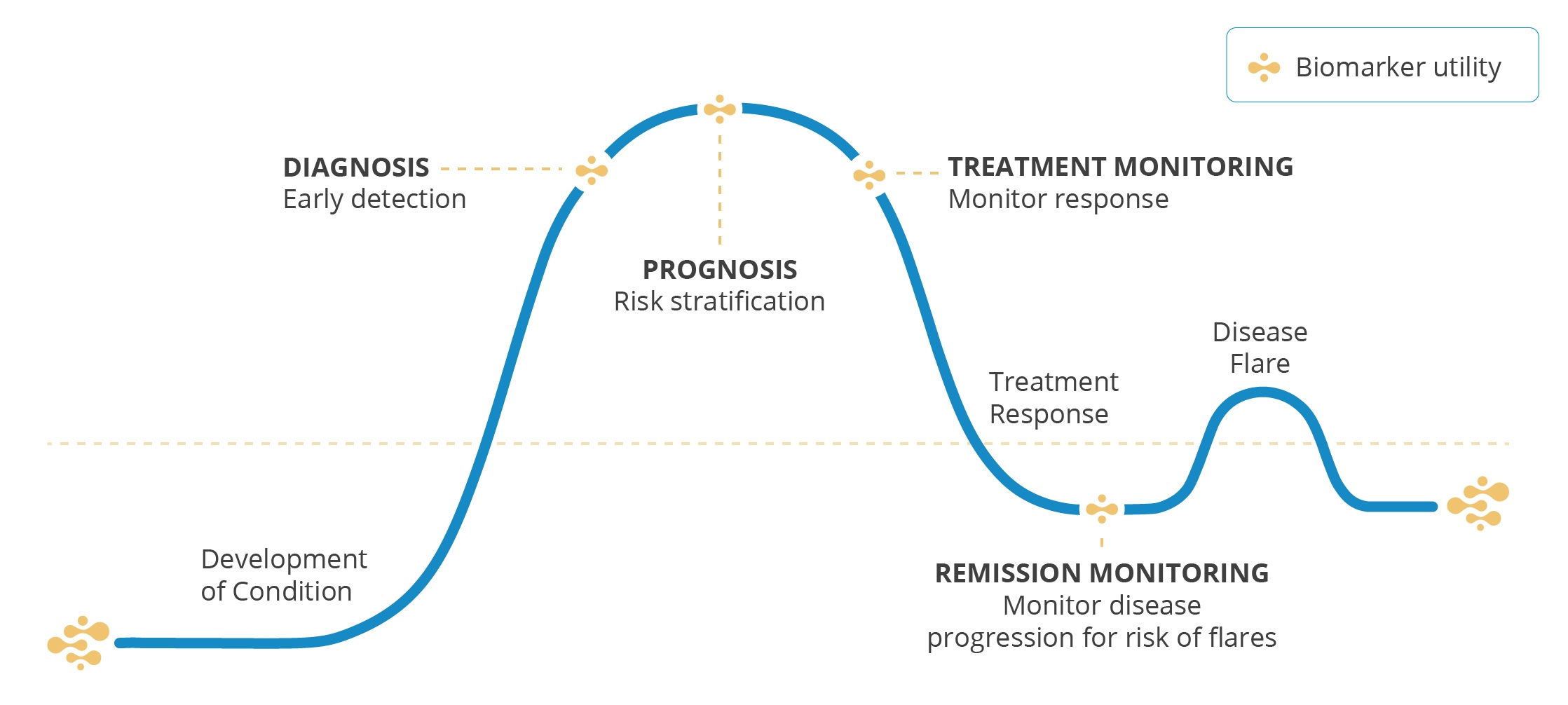
Providing critical insights across the continuum of patient care for diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis.

Clinical gaps in RA and the Patient Impact
Early RA Diagnosis
Prognosis
Treatment Monitoring
Flares and Risk of Damage
Flares are common and difficult to predict, increasing the likelihood of ongoing joint damage.
26% to 39% of individuals with RA experience flares within one to two years of remission, with frequent flares increasing the risk of radiographic progression.9,10
Supporting the Continuum of Care and Patient Journey
14-3-3eta is a mechanistic and modifiable biomarker, providing clinical utility from early diagnosis to remission
14-3-3eta complements RF and anti-CCP to enable earlier, more accurate diagnosis of RA
High Sensitivity & Specificity
Seronegative RA
Complements Existing Markers
Predictive Value



14-3-3eta is modifiable and its levels inform disease severity and therapy response

Example of serial testing of 14-3-3eta every 3 months
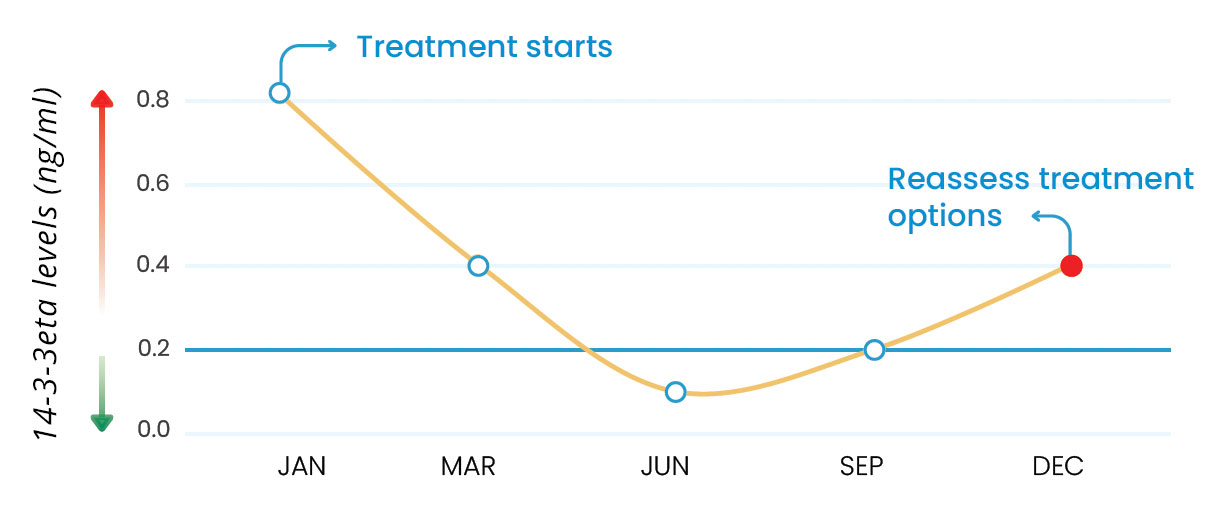
14-3-3eta is a modifiable biomarker and an independent predictor of disease progression and joint damage risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Because its levels respond to treatment, serial testing helps closely monitor how well a patient is responding to therapy.
Combining 14-3-3eta with CRP improves joint damage prediction and supports tight-control treatment strategies:
- Decreases in 14-3-3eta levels in response to therapy are associated with better clinical outcomes.16-18
- Increases or sustained 14-3-3eta levels, particularly ≥ 0.50 ng/mL, indicates significant joint damage risk and are associated with a worse prognosis.19,20
- High CRP (>8.0 mg/L) combined with elevated 14-3-3eta (≥0.50 ng/mL) represents an adverse prognostic signature, and together, these markers provide better prediction of joint damage than either marker alone.19,20
Strategies for effective remission maintenance and flare risk prediction
Guidance for Remission Maintenance
Monitoring 14-3-3eta and CRP can help identify patients at higher risk of radiographic progression, aiding in more informed decisions on dose tapering and remission maintenance.19,20
Predictive Value for Flare Risk
Higher 14-3-3eta levels at baseline, especially when combined with low CRP, are strong predictors of flare risk in patients discontinuing biologic therapy.15
14-3-3eta Resources
The 14-3-3eta protein is a joint-derived, proinflammatory mediator that is implicated in the joint erosion process and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.14
Learn how the 14-3-3eta test can aid in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and inform clinical decisions at every stage of care.
References
References:
- World Health Organization. Rheumatoid arthritis. 2023, June 28. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rheumatoid-arthritis
- Arthritis Foundation. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments and More. 2021, Oct 15. https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/rheumatoid-arthritis
- Arthritis Society Canada. Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms and Diagnosis. 2023, Sep. https://arthritis.ca/about-arthritis/arthritis-types-(a-z)/types/rheumatoid-arthritis/rheumatoid-arthritis-symptoms-and-diagnosis
- UpToDate. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. 2024, Mar 21. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis
- Arthritis Foundation. Your RA is in Remission! Now What? https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/treatment-plan/disease-management/your-ra-is-in-remission!-now-what
- Ursum J, Bos WH, van Dillen N, Dijkmans BA, van Schaardenburg D. Levels of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and IgM rheumatoid factor are not associated with outcome in early arthritis patients: a cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):R8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20064278/
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960-977. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36357155/
- Mease PJ, Stryker S, Liu M, et al. Treatment patterns in rheumatoid arthritis patients newly initiated on biologic and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy and enrolled in a North American clinical registry. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):236. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34496952/
- Chaiamnuay S, Jiemjit S, Songdechaphipat W, Narongroeknawin P, Pakchotanon R, Asavatanabodee P. Predictors of flare in rheumatoid arthritis patients with persistent clinical remission/low disease activity: Data from the TARAC cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(32):e29974. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35960097/
- Smolen JS, Pedersen R, Jones H, Mahgoub E, Marshall L. Impact of flare on radiographic progression after etanercept continuation, tapering or withdrawal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(1):153-164. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31257453/
- Maksymowych WP, van der Heijde D, Allaart CF, et al. 14-3-3η is a novel mediator associated with the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and joint damage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4060379/
- Maksymowych WP, Naides SJ, Bykerk V, et al. Serum 14-3-3η is a novel marker that complements current serological measurements to enhance detection of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(11):2104-2113. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25128504/
- Abdelhafiz D, Kilborn S, Bukhari M. The Role of 14-3-3 η as a Biomarker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2021;2(2):87-90. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9524784/
- Naides SJ, Marotta A. 14-3-3η in “Seronegative” Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(10):1995. https://www.jrheum.org/content/42/10/1995.2
- Hirata S, Marotta A, Hanami K, et al. SAT0062: 14-3-3ETA predicts joint damage progression and flaring after adalimumab discontinuation. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017;76:791. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003496724240188
- Sornasse T, Chahal S, Gui Y, et al. AB0104: Correlation of plasma 14-3-3η levels with disease activity measures in methotrexate-naïve RA patients treated with upadacitinib monotherapy in the SELECT-EARLY phase 3 study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2020;79:1351. https://ard.bmj.com/content/79/Suppl_1/1351.2
- Hirata S, Marotta A, Gui Y, Hanami K, Tanaka Y. Serum 14-3-3η level is associated with severity and clinical outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis, and its pretreatment level is predictive of DAS28 remission with tocilizumab. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:280. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26449724/
- Shovman O, Gilburd B, Watad A, et al. Decrease in 14-3-3η protein levels is correlated with improvement in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with Tofacitinib. Pharmacol Res. 2019;141:623-626. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30414892/
- Carrier N, Marotta A, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, et al. Serum levels of 14-3-3η protein supplement C-reactive protein and rheumatoid arthritis-associated antibodies to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26832367/
- Carrier N, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, Liang P, et al. Impending radiographic erosive progression over the following year in a cohort of consecutive patients with inflammatory polyarthritis: prediction by serum biomarkers. RMD Open. 2020;6(1):e001191. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32371434/
Ordering information for providers