Our Science
Our 14-3-3eta biomarker portfolio features the joint-derived 14-3-3eta protein and its autoantibodies, providing insights into the disease mechanisms of inflammatory autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis.
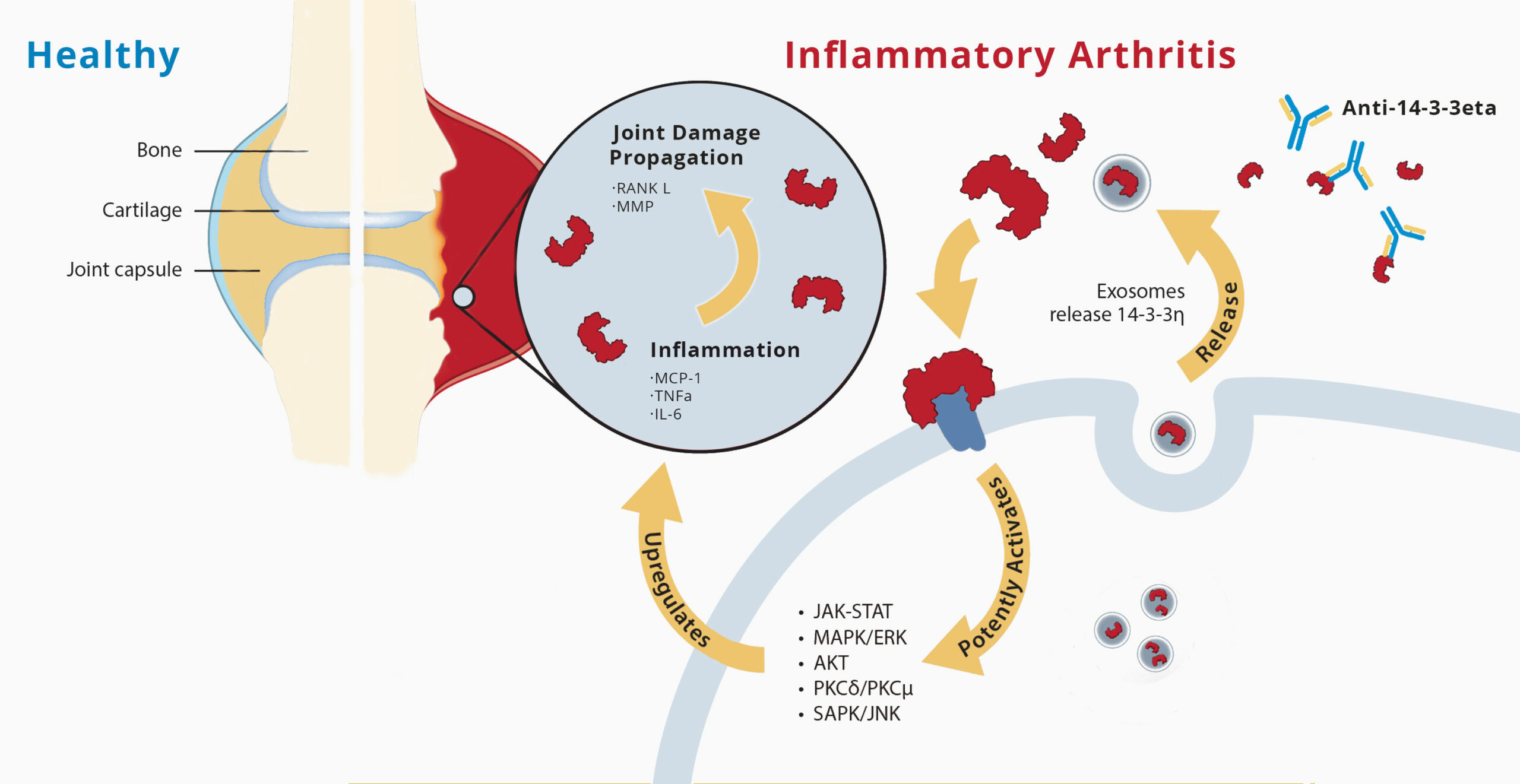
14-3-3eta Biomarker Portfolio: Precision Diagnostics for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis
The 14-3-3eta protein is a joint-derived intracellular protein involved in essential cell functions. During joint inflammation, it is externalized and acts as a proinflammatory ligand, driving further joint erosion and damage.
Its utility as a biomarker was established when elevated levels in serum and synovial fluid were shown to be highly specific to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), distinguishing it from other inflammatory conditions and arthritides. The presence of 14-3-3eta was prominently linked to active joint inflammation and damage risk. As 14-3-3eta levels fluctuate, it helps monitor disease activity and response to treatment, providing insights into ongoing joint damage risk in RA.
Autoantibodies to 14-3-3eta epitopes (anti-14-3-3eta) have also been identified as a novel biomarker for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), which when used in a diagnostic test could reduce the typically extensive delay in diagnosis and enable earlier intervention.

Learn more about how our products can transform patient outcomes. Our testing solutions feature the 14-3-3eta test for diagnosing and monitoring rheumatoid arthritis (JOINTstat), as well as our first-in-class diagnostic test for axial spondyloarthritis (SPINEstat).
Publications
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Over 10 years of peer reviewed research
14-3-3η Mechanism of Action
- 14-3-3η is a Novel Mediator Associated with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Joint Damage
- 14-3-3η Promotes Invadosome Formation via the FOXO3–Snail Axis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes
- Tumour necrosis factor alpha promotes secretion of 14-3-3η by inducing necroptosis in macrophages
Risk of RA
Diagnosis
- Serum 14-3-3η is a Novel Marker that Complements Current Serological Measurements to Enhance Detection of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 14-3-3η Autoantibodies: Diagnostic Use in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis
- The Diagnostic Value of 14-3-3η Protein Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Serum 14-3-3η Protein is Associated with Clinical and Serologic Features of Sjögren’s Syndrome in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
- Evaluation of Serum Protein 14-3-3 Eta as a Novel Biomarker for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Anti-Carbamylated Protein (Anti-CarP) Antibodies in Patients Evaluated for Suspected Rheumatoid Arthritis
Prognosis
- Serum Levels of 14-3-3η Protein Supplement C-reactive Protein and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Antibodies to Predict Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes in a Prospective Cohort of Patients with Recent-Onset Inflammatory Polyarthritis
- Impending Radiographic Erosive Progression Over the Following Year in a Cohort of Consecutive Patients with Inflammatory Polyarthritis: Prediction by Serum Biomarkers
- Serum 14-3-3η as predictor of clinical remission and progression of structural damage in early rheumatoid arthritis following a treat-to-target strategy in a randomized controlled trial
Monitoring
- Serum 14-3-3η Level is Associated with Severity and Clinical Outcomes of Rheumatoid Arthritis, and its Pretreatment Level is Predictive of DAS28 Remission with Tocilizumab
- Decrease in 14-3-3η Protein Levels is Correlated with Improvement in Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tofacitinib
- Correlation of Plasma 14-3-3η Levels with Disease Activity Measures in Methotrexate-Naïve RA Patients Treated with Upadacitinib Monotherapy in the Select-Early Phase 3 Study
Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis
Axial Spondyloarthritis
Newest addition to our portfolio
Diagnosis
- Auto-Antibodies to A Specific 14-3-3Eta Epitope is A Marker of Ankylosing Spondylitis, is Associated with SIJ Inflammation and Predicts Radiographic Progression
- Novel Diagnostic 14-3-3η Auto-Antibody Marker for Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Longitudinal Study. (Fourteenth International Congress on Spondyloarthritides)
- Autoantibodies to 14-3-3η in Axial Spondyloarthritis
- 14-3-3 Eta (η) Auto-Antibody as a Diagnostic Marker in Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Longitudinal Study

